Key Components of ABDM Implementation
1. ABHA (Ayushman Bharat Health Account) ID
-
Every citizen can generate a unique health ID (ABHA), linked to their medical records.
-
Enables secure and seamless access to personal health records across different healthcare providers.
2. Unified Health Interface (UHI)
-
A digital backbone allowing different health applications and service providers to communicate.
-
Standardized APIs ensure interoperability between hospitals, labs, telemedicine providers, and insurance companies.
3. Health Facility Registry (HFR) & Healthcare Professional Registry (HPR)
-
HFR: A national database of hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers for easy discovery and verification.
-
HPR: A centralized registry for doctors and healthcare professionals for authentication and digital engagement.
4. Personal Health Records (PHR) System
-
Secure digital storage and sharing of medical records.
-
Patients have control over data access and consent management for hospitals, doctors, and insurance providers.
5. ABDM Sandbox for Developers
-
An open digital platform for tech companies to test and integrate healthcare applications with ABDM’s ecosystem.
-
Encourages innovation in EHR, telemedicine, and health insurance platforms.
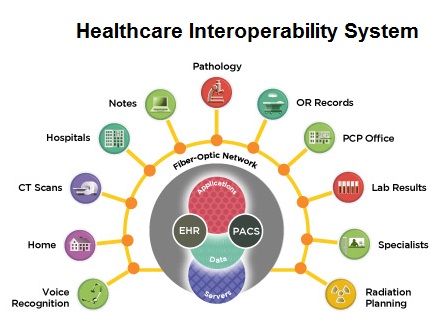
Impact on Healthcare Interoperability
1. Seamless Data Exchange Between Health Providers
-
ABDM standardizes the exchange of medical data using FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources).
-
Reduces redundancy by enabling hospitals, diagnostic centers, and doctors to access a patient’s medical history instantly.
2. Better Coordination Between Public and Private Healthcare
-
Private hospitals, government facilities, and insurance providers can access a common digital health infrastructure.
-
Enables faster claims processing and fraud detection through real-time data verification.
3. Increased Adoption of Telemedicine and Digital Health Services
-
Remote consultations and online prescriptions are now more effective due to a unified digital framework.
-
Patients can share their ABHA-linked health records with doctors instantly, improving diagnosis accuracy.
4. Improved Efficiency in Health Insurance and Claims Processing
-
Automated verification of patient eligibility under schemes like PM-JAY and private health insurance.
-
Reduces delays in claims adjudication and minimizes fraudulent transactions.
5. Strengthened Data Privacy and Patient Control
-
Decentralized data management ensures that patients have complete control over their health records.
-
Consent-based access ensures GDPR-like privacy compliance, preventing unauthorized data sharing.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Challenges:
-
Digital divide: Rural areas may face challenges in adopting ABDM due to low digital literacy.
-
Integration hurdles: Existing hospital IT systems, PACS, and insurance databases need upgrades for full compatibility.
-
Cybersecurity concerns: Ensuring data protection against cyber threats is crucial.
Future Scope:
-
AI-powered analytics for personalized treatment recommendations.
-
Blockchain-based security to enhance data integrity and prevent tampering.
-
IoT integration for real-time health monitoring and emergency response systems.
Conclusion
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) is a game-changer in India's healthcare ecosystem, driving interoperability, efficiency, and accessibility. By integrating hospitals, diagnostic centers, insurers, and telemedicine platforms, ABDM is revolutionizing patient care, digital health records, and insurance claims processing. While challenges remain, the long-term impact will lead to a more connected, efficient, and transparent healthcare system in India.